how to control blood sugar levels with insulin How to lower blood sugar: how does insulin control blood sugar levels
How To Lower Blood Sugar: How Does Insulin Control Blood Sugar Levels
Image 1
 Insulin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels. It is produced by the pancreas and helps regulate the amount of glucose in the blood. Understanding how insulin works can provide valuable insights into managing blood sugar levels and preventing conditions like diabetes.
Insulin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels. It is produced by the pancreas and helps regulate the amount of glucose in the blood. Understanding how insulin works can provide valuable insights into managing blood sugar levels and preventing conditions like diabetes.
When we consume food, especially those high in carbohydrates, the body breaks down the carbohydrates into glucose. This glucose is then released into the bloodstream, leading to a rise in blood sugar levels. To counterbalance this increase, the pancreas secretes insulin.
Image 2
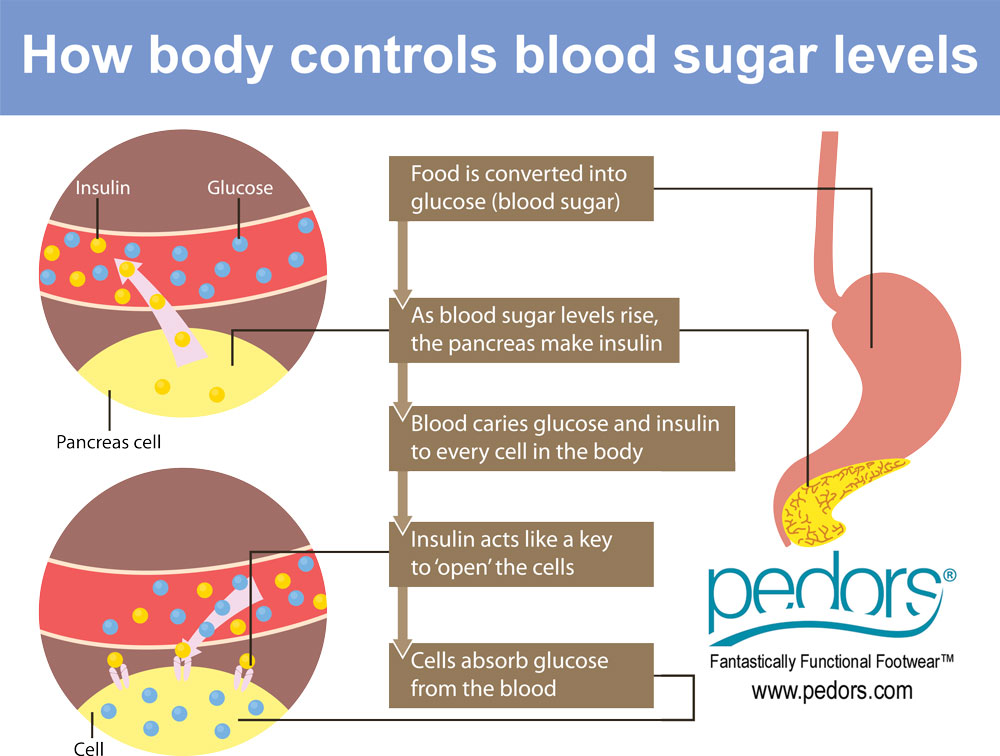 The role of insulin is to enable the cells in our body to absorb glucose from the bloodstream and use it as a source of energy. It acts as a key that unlocks the cells, allowing glucose to enter. Without insulin, glucose would remain in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
The role of insulin is to enable the cells in our body to absorb glucose from the bloodstream and use it as a source of energy. It acts as a key that unlocks the cells, allowing glucose to enter. Without insulin, glucose would remain in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Insulin also plays a vital role in facilitating the storage of excess glucose. When blood sugar levels are high, insulin signals the liver, muscles, and fat cells to take in the excess glucose and store it as glycogen. This stored glycogen can be used as a future energy source when needed.
In individuals with diabetes, however, the body either does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or becomes resistant to insulin’s effects (Type 2 diabetes). Consequently, glucose remains in the bloodstream, leading to persistently high blood sugar levels.
To effectively manage blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes may need to take insulin injections or use insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring systems. These devices help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications associated with diabetes.
It is essential for individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, adjust insulin doses as necessary, and follow a healthy lifestyle consisting of a balanced diet and regular exercise. By maintaining optimal blood sugar control, individuals can reduce the risk of long-term complications such as heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney problems.
In conclusion, understanding how insulin controls blood sugar levels is key to managing diabetes and preventing complications. Insulin acts as a gatekeeper, allowing glucose to enter cells and facilitating the storage of excess glucose. Individuals with diabetes may need external sources of insulin to regulate their blood sugar levels effectively. Regular monitoring, insulin therapy, and a healthy lifestyle are integral components of blood sugar management.
If you are looking for #113 The control of blood glucose | Biology Notes for A level you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pics about #113 The control of blood glucose | Biology Notes for A level like #113 The control of blood glucose | Biology Notes for A level, Diabetes - A Simple Guide To Understanding Diabetes - Pedors Shoes Store and also Diabetes - A Simple Guide To Understanding Diabetes - Pedors Shoes Store. Read more:
#113 The Control Of Blood Glucose | Biology Notes For A Level
 biology4alevel.blogspot.comblood glucose control summary homeostasis level sugar cycle does liver low concentration insulin loop fuel feedback break physiology regulate eating
biology4alevel.blogspot.comblood glucose control summary homeostasis level sugar cycle does liver low concentration insulin loop fuel feedback break physiology regulate eating
How To Lower Blood Sugar: How Does Insulin Control Blood Sugar Levels
 howtolowerbloodsugarquick.blogspot.cominsulin
howtolowerbloodsugarquick.blogspot.cominsulin
Manage Blood Sugar : Control Blood Glucose Levels Insulin
managebloodsugars.blogspot.comdiabetes glucose
Blood Sugar Secret: How Does Insulin Control Blood Sugar Levels Gcse
bloodsugarssecret.blogspot.cominsulin gcse
Diabetes - A Simple Guide To Understanding Diabetes - Pedors Shoes Store
 www.pedors.comdiabetes simple blood insulin sugar body understanding levels controlling relationship controls guide between
www.pedors.comdiabetes simple blood insulin sugar body understanding levels controlling relationship controls guide between
Blood glucose control summary homeostasis level sugar cycle does liver low concentration insulin loop fuel feedback break physiology regulate eating. Insulin gcse. Manage blood sugar : control blood glucose levels insulin